Confused difference between CV, Resume, and Biodata? Even I was, let me explain to you in detail so that you never get confused again.
Curriculum Vitae
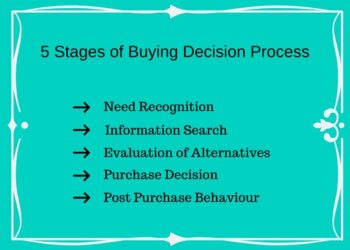
CV or Curriculum Vitae essentially means “Course of Life”. Therefore, a CV should be a micro summarization of your own life experiences in a stretch of a few pages. CV is used to describe one’s life activities in a few pages to let the employer know the employee better. It is akin to a Biography which will be used by one only for job purposes. Hence, any experience which is pertinent to one’s job must be typed in one’s CV.
CV is written in a general fashion that caters to the needs of every company at one go. Hence, it is not customized for each and every company. The next pertinent issue is by whom is CV generally prepared and what it is used for.
1) A CV is most commonly used by college pass outs that are looking forward to entering the field of work soon. It can also be suitable for someone who has been out of the industry or occupational field for quite a considerable length of time. Though it is more or less like a Biography that tells the recruiter about your life experiences still there are certain things that you should refrain from putting up in your CV.
Your CV must be consistent with the current trends of the industry or field you belong to. It must be short and simple and must only contain your life experiences relevant to your job. Otherwise, your recruiter would be confused about what you actually want from that particular job.
2) Although there is no restriction on the length of your CV, it should not be less than 1 page. A CV is generally 3-6 pages long and it informs the recruiter about your life’s timeline in a nutshell. Your CV must be too fancy or too dull. It should be written to the point.
3) CV is deliberately made simple for the recruiter to understand and process every experience carefully. CV, however, can be customized according to one’s own self to make it look more attractive and elegant. It must be engaging so that the reader reads it to the end.
4) Your CV should mention your career objectives very clearly and must be customized according to the job you are applying for. Your career objectives might be different from the job you are applying for but you must, through your CV, explain it clearly that the job you are applying for is conducive to your long-term career goals.
It should be clear from your CV that you are interested and serious about the post you are applying for. You can explain to your employer that your current job will help you achieve your end goal.
5) Your talents and skill set must be mentioned next in your CV. The talents and skills which you possess which are relevant to the corporate sector must be mentioned in your CV. Mention your feats and achievements in detail.
6) You can mention your experiences chronologically or they can be categorized according to different types. You need to mention all your experience in detail without using elaborate and tough words. You must furnish all your information to the recruiter in a bulleted list which will help your recruiter to make an informed decision.
7) Your CV must be accompanied by a cover letter that presents your CV on a single page. This will enable your recruiter to pick your CV faster than the people who have not typed out a cover letter.
Resume
A resume is a French word that evidently means summary in English. As the name suggests a Resume summarizes all your deeds and skills in a small number of pages. A resume serves the purpose for those people who have experience in the field already but are searching for new options in the same industry where skills matter the most rather than academic achievements.
A Resume is very different from the other two formats. A resume is very rich in content and it puts to use the essential skills and experiences that are penned down in the Resume to facilitate the recruiter to know the candidate better.
Difference between a CV and a Resume in Points
a) Unlike a CV a Resume consists of information in a very precise and condensed manner. You must be an experienced candidate if you prepare a Resume. It is not for freshers at all.
A resume contains the choicest set of skills and experiences that are relevant to the particular job you are applying for. You need to mention all your talents and showcase them in a manner that is crisp and to the point.
b) A CV generally describes your whole life’s experiences whereas a Resume showcases the things which will impress only your employer or recruiter. It should be unique and must be designed in such a way that no Resume should be an exact copy of each other. It should contain only experiences and skills pertinent to your job.
c) Unlike a CV, a Resume goes up to one page and a maximum of up to 3 pages. No recruiter will read a Resume that is extremely verbose and lengthy. It should have precise and accurate information about your set of skills and experiences.
d) Unlike a CV, a Resume format can be varied whereas in a CV the format is more or less fixed and stable. The main thing to be kept in mind while making a Resume is that the Resume should be accurate, reliable, and attractive in all respects so that your recruiter gets a crystal clear impression of your relevant skills and experiences.
e) You should make your resume eye-catching and elegant at the same time. It should be elegant enough for the recruiter to skim through your information within no time. The layout of the resume decides whether you will be selected for the interview or not.
f) Unlike a CV, you can write your experiences and skills in the resume in reverse chronological order to make sure to display which skills are important to you at the present. The skills can also be written in functional order where the candidate explains how his or her skills will help the employer in fulfilling their job requirements.
g) People sometimes prefer a Functional Resume with a chronological order in mind. A resume should reflect your effort and achievements in your field nevertheless. It should show the fact that how your skills will be helpful for the company.
h) The only thing which makes a Resume quite different from other formats is its practicality in use. Numerous candidates apply for a single job at a go. Therefore, it is not possible to skim through big CVs. A resume comes in handy in this aspect. It helps recruiters to shortlist suitable candidates easily.
i) Due to the advent of technology it has become quite easy to choose the right candidates among millions of aspirants using certain keywords and SEO-friendly resumes. The SEO-optimized resume stands out from the rest of the applicants which helps the recruiter to spot the best candidate sooner.
Biodata
Biodata is short for Biological Data. It is an old and archaic version of the Resume and Curriculum Vitae. It is a short commentary about life and its events. It was used earlier for job purposes but now it is only restricted to certain fields. It speaks a lot about the personal details of the person concerned.
Biodata is generally used presently in Government institutions and in marriage purposes as well. It specifically focuses on providing personal details to people who want to know the details.
Difference between Biodata and the other formats (CV and Resume)
a) Biodata commonly consists of a person’s personal details like name, age, caste, creed, academic details, gender, and other information which is sensitive in nature and must not be disclosed easily. After penning down all your personal details only then you can proceed on to show off your academic experiences and other relevant skills which are pertinent to the field you are applying for.
You should also share your life experiences as well in chronological order of the events. Due to the personal nature of the data provided, you can only use biodata in institutions where you absolutely need it like when you apply for a driving license or bank account, etc. Your data mentioned in your CV or Resume are not that person in nature so they are mostly used for job purposes.
b) One must be extremely careful while disclosing one’s data in a biodata. You must make sure that your information is somehow protected and secure to avoid any kind of fraudulent activity.
c) Unlike a CV or a Resume, this format cannot be customized by an individual but by an institution. This makes it simple and easier to collect the data in a methodological and systematic manner. You can keep track or record your data on computers in an electronic format as well. A well-written biodata will contain ample information about one’s skills and talents which a CV or a Resume often fails to provide.
d) A Biodata generally consists of 1 to 3 pages depending upon the density of information provided in it and also on what type of information is needed by the institution.
e) One of the drawbacks of Biodata is that it is an outdated format and therefore, a lot of companies refuse to accept it as a means of criteria for candidate selection. This is due to the fact that firstly, it does not allow the candidate space for describing his job abilities and skills at length.
Secondly, many states have made it absolutely mandatory to avoid putting up sensitive information like your PAN card number or other sensitive details in your job application to protect your privacy. One should only provide essential information which is relevant to the particular job.
The main points of difference between a CV, Resume and Bio-data
All three formats seem very similar in nature but there are some essential points of difference among the three formats.
a) A CV is the longer of the two formats and is used mainly to narrate one’s life events. It is generally used by Freshers who are just starting off in the job-hunting process. It is generally lengthy consisting of 3 to 6 pages. It is ideal for a CV to be accompanied by a cover letter to boost up your chances of bagging a great job.
CV is not tailor-made for a single company but it is more general in format. It provides an overall idea about the person rather than the skills and experiences he or she possesses.
b) Resume essentially means summary and is the shorter of the two aforementioned formats. It does not extend beyond a single page. It is used by experienced candidates who are looking for better job opportunities or a career change. A recruiter skims through the Resume to know the skills and experiences of the person concerned better. Therefore, a Resume must be crisp, concise, and simple.
c) Biodata is an outdated version of the other two formats. Biodata stands for Biographical Data. It contains the personal information of employees like name, sex, age, gender, caste, etc. Its usage is limited to marriage meetings and Government institutions. It is generally not accepted by corporate companies nowadays.
These are the differences in the three formats used to apply for a job in the market. Now that we have given you all the information about the three formats now you can choose your desired format and start applying for a job according to your need. Hope so this article cleared all your doubts and worries. If you still have some queries we have got you covered in the next FAQ section. So, stay tuned!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What does Bio-data include?
Ans –. Biodata is essentially known as Biological Data. It consists of largely the immensely personal information of employees like their own name, sex, age, gender, caste, and other information pertaining to one person. Its usage is limited to marriage meetings and Government institutions.
2. What is the difference between CV and Profile?
Ans – A CV is tailored and sent directly to an individual business, whereas your online profile has the potential to attract and engage a much wider audience. It can attract multiple companies at a go. A profile is generally created to attract consumers of a particular service or product. It can be made on various platforms to attract recruiters as well such as LinkedIn, Upwork, etc.
A profile should be precise and well-written so that it provides general attraction to the public. It should engage the public and recruiters to come to you to provide a job that suits your need. A CV is presented by an individual to a single recruiter at a time for that specific job role. A profile is much more necessary than a CV to earn more followers and gain more valuable connections.
3. Which is better – a CV or a Resume?
Ans – A CV is used to enumerate one’s life events and is generally longer than a Resume. It is basically of utmost importance to Freshers who are newly starting off in the job market and also to people who want to start off their career on a different path. A CV consists of 3 to 6 pages. A CV is ideally accompanied by a cover letter to kick start the chances for a fresher to grab a job opportunity as early as possible.
A CV is not customized for a single company but it is written in a general form. On the other hand, a Resume is shorter than a CV and basically means a summary. It is short and does not exceed one page. It is essentially used by candidates who already have experience in the job market and are looking out for a career boost or change.
A person who recruits a candidate goes through the resume and decides whether the candidate is fit for that particular post. Hence, a Resume must be extremely short, simple, and concise. Both of the formats can be used by a job-seeker with a bit of understanding.
4. What is meant by Biodata?
Ans. – Biodata essentially means Biological data. It is an obsolete format used in the olden days for jobs. Now, it is used in marriage meetings and to generate Government documents. It includes the personal information of individuals like age, name, sex, caste, etc.
5. Can I use a Resume instead of a CV?
Ans. – In general, you would use a CV and a Resume in the following situations:
A CV is basically required when applying for international, academic, scientific, or research positions whereas a resume is a preferred format to apply for most jobs in the U.S. and Canada. You can use a Resume for skilled jobs whereas you can use a CV for more detailed jobs like Research and allied purposes. A CV is a more general format of job application rather than a Resume.
6. How do I turn my Resume into a CV?
Ans. – Common components of each CV and Resume
Resumes and CVs are both usually sorted out by category.
Common categories for a resume include:
- Heading
- Education
- Work experience
- Volunteer experience
- Skills
Common CV categories include:
- Heading
- Education
- Work experience
- Honors and awards
- Research
- Publications
- Presentations
- Grants
- Certifications and licenses
- Associations
- Volunteer experience
- References
To convert a Resume into a CV you need to follow the following steps:
- Copy the heading of the CV
- Include educational Qualifications
- List work experiences
- Add honors, awards, and recognition which you have achieved
- Include research papers published
- List presentations that you have already presented
- Provide Detail about grants which you have received
- Provide any licenses and certifications which you have done
- List associations and connections
- Copy volunteer work that you have already done
- Provide references, include a list of professional references
7. Which is bigger – a CV or a Resume?
Ans – Curriculum Vitae (CV) outlines the academic qualifications, research, and other relevant details about a person, to represent him in front of recruiters. A CV is generally 3 to 6 pages long and much more detailed.
A Resume is a precise document, which underlines a person’s qualifications for a specific job. It consists of at the most 1 to 2 pages and is extremely precise and well written according to the needs of the employers. When it comes to length, a CV is much larger than a resume and is often preferred by academic recruiters or jobs. A resume is preferred more by corporate sector recruiters.
8. Can I submit a Resume instead of a CV?
Ans. – The answer to this question with all due respect is a big ‘NO’. A CV is the longer of the two formats and is used mainly to narrate one’s life events for academic purposes. It is generally used by beginners who are just starting off in the job-hunting process. It is generally lengthy consisting of 3 to 6 pages. It is ideal for a CV to be accompanied by a cover letter to boost up your chances of bagging a great job.
CV is not tailor-made for a single company but it is more general in format whereas a Resume essentially means summary and is the shorter of the two aforementioned formats. It does not extend beyond a single page. It is used by experienced candidates who are looking for better job opportunities or a career change.
A recruiter skims through the Resume to know the skills and experiences of the person concerned better. Therefore, a Resume must be crisp, concise, and simple. Both formats are good and must be used by a candidate with discretion. It is a must for the candidate to make a well-informed choice as to when to use a CV and when to use a Resume.
Hope so your doubts were cleared up by this article. See you guys in the next one. Till then keep fighting and all the very best for your future endeavors!
[ Also Checkout: 7 Questions To Ask Yourself Before Picking Up A Career ]